Researchers at the University of New South Wales (UNSW) in Australia once again broke the energy efficiency record of photovoltaic cells and raised solar conversion efficiency to a staggering 34.5%. Previously, Alta Devices in the United States had set a record of 24% conversion rate, but the new equipment created by Mark Weevers and Martin Green, senior researchers at the Advanced Solar Optics Center of the United Nations in Australia, also improved performance. In 2014, they used mirrors to concentrate light and set the conversion rate at more than 40%. This time, however, the new device did not “cheat,†but it was achieved under normal lighting conditions.

UNSW's Mark Keevers showed off his device.
Keevers stated in a statement: "This encouraging result shows that our research in photovoltaic power generation is still progressing and can make solar cells more efficient."
“By converting each beam of light into as much energy as possible, it is extremely important to reduce the cost of solar power generation because it reduces the investment needed and the return is faster.â€
The new device is a combination of four mini-modules embedded in a prism (28cm2 in size). When the sun shines on the prism, it is split into four quadruple input receivers, increasing the amount of energy available from the sun.
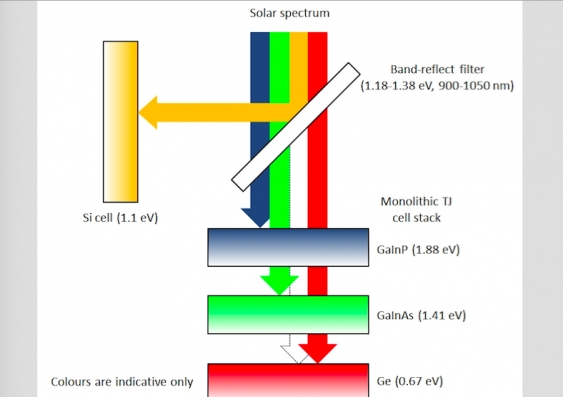
Work diagram of the new device.
On one side of the glass prism is a silicon cell; on the other side is a triple-junction solar cell.
This type of solar cell has three layers, each corresponding to different light waves, which can make the most efficient use of light energy, and the remaining light energy will be transmitted to the next layer, and the final infrared light wave will be screened and bounced back to the silicon photocell.
Unfortunately, due to the complexity of the structure and the high cost of mass production, the current prototype device is not suitable for large-scale application on the roof, but the team is trying to reduce its complexity.
At the same time, researchers plan to expand the scale of the device even more. For example, Alta Devices' photovoltaic cells have an area of ​​800cm2. If UNSW’s new installation can also reach this scale, it is expected to further reduce the marginal loss.
Green said: “The industry has not been able to achieve this level of efficiency for many years, and a recent study by Agora Energiewende in Germany also believes that by 2050 it will be possible to achieve a 35% efficiency of non-focus solar collection modules and go into home applications†.
Taps and dies are tools used to create purpose screw threads, which is called threading. Many are cutting tools; others are forming tools. A tap is used to cut or form the female portion of the mating pair (e.g. a nut). A die is used to cut or form the male portion of the mating pair (e.g. a bolt). The process of cutting or forming threads using a tap is called tapping, whereas the process using a die is called threading.
Using an ordinary tap or die to clean threads generally removes some material, which results in looser, weaker threads. Because of this, machinists generally clean threads with special taps and dies-called chasers-made for that purpose.
Drill And Tap Set,Hand Tap And Die,Cutting Tool Sets,Hand Tap Wrench
Behappy Crafts (suzhou)Co.,Ltd , https://www.haoyuebehappy.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)