In the northern winter wheat area, the light temperature is sufficient, and most of the soil has good moisture conditions, which is conducive to the return of winter wheat. Most of the southern regions are dominated by weather and rain, which is beneficial to the growth and development of winter wheat and rapeseed and spring sowing. Only some areas have strong adverse effects on early rice planting and rapeseed and rapeseed. There is only weak precipitation in northern Yunnan and southern Sichuan, and the drought continues, which is not conducive to winter wheat yield formation and spring sowing.
Main weather characteristics of this week
Temperatures in most agricultural areas are high (Fig. 1), and temperatures in the northeastern region and eastern Inner Mongolia are only 2 to 4 °C lower than normal. Precipitation mainly occurs in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River and its south (Fig. 2). Heavy rains occur in parts of the south and south of the Yangtze River. The rainy days in Fujian, Jiangxi, eastern Guangxi, southern Hunan, and southwestern Zhejiang are more than 5 days. 3); significant precipitation occurred in central and southern Yunnan, and drought in some areas eased. Most of the country's agricultural areas have sufficient sunshine, and the sunshine in Chongqing, Guangdong and Guangxi is less than 30 hours, which is close to the normal period or slightly less (Figure 4). 
Figure 1 Average temperature anomaly in early April 2012 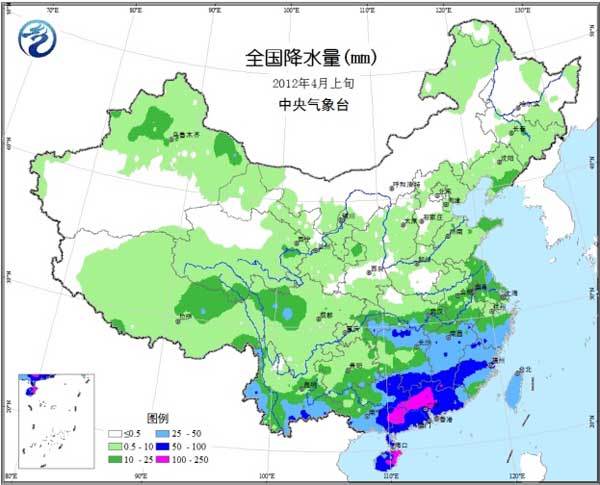
Figure 2 Precipitation in early April 2012 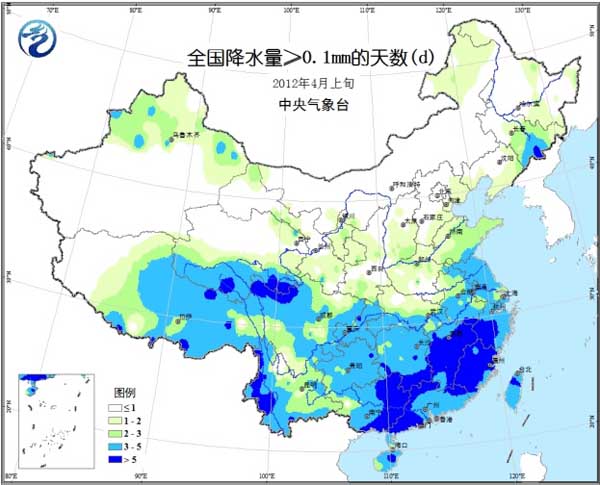
Figure 3 Rainy days in early April 2012 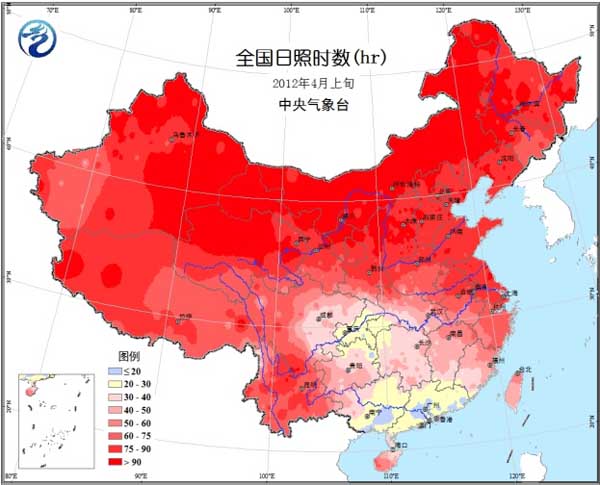
Figure 4 Sunshine hours in early April 2012
Current crop growth and development report
Winter wheat: Xinjiang, the northwestern part of the country, and northern China are in the period of greening to jointing; the southern part of Huanghuai, Jianghuai and Jianghan are in the jointing stage; the south of Jianghan and the north-central part of the southwest are in the heading stage, and most of Yunnan is in the stage of maturity to maturity (figure 5).
Spring wheat: The northwestern region and southeastern Inner Mongolia are in the stage of sowing and emergence (Fig. 6). 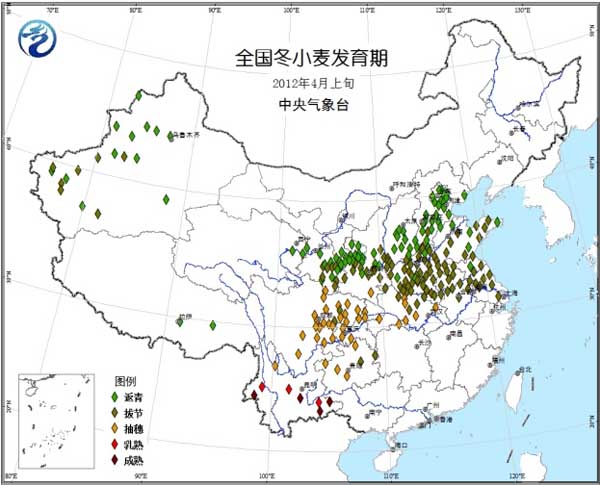
Figure 5 Winter wheat development period in early April, 2012 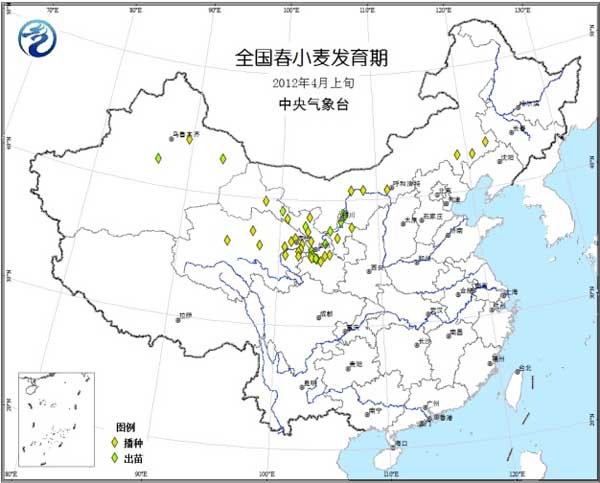
Figure 6 Spring wheat development period in early April 2012
Rapeseed: The middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, the southwestern part of Shaanxi, and the southwestern part of the country are generally in flowering (Fig. 7).
Spring maize: the eastern part of the Sichuan Basin is in the period of emergence to the three-leaf stage, the western part of Guangxi is in the period of three-leaf to seven-leaf, and the northwest is in the sowing period (Fig. 8).
Early rice: most of the south of the Yangtze River and northern part of South China are in the stage of sowing and breeding, the middle part of South China is in the stage of transplanting and returning to the green, the south is in the tillering to heading stage, and the part of Hainan is in the stage of milk ripening (Fig. 9).
One season of rice: the Sichuan Basin and most of the central and northern Yunnan are in the stage of seedling growth, and the southern part of Yunnan has entered the transplanting and returning stage and partially entered the tillering stage (Fig. 10).
Cotton: The Xinjiang and Yellow River Basins are in the sowing period (Figure 11).
Potatoes: The southeastern part of the southwestern region and southern Gansu are in the seedling emergence stage, and the Yunnan part enters the inflorescence formation stage (Fig. 12).
Tobacco: Yunnan, Guizhou, Chongqing, Henan and other places are in the second true leaf stage, Anhui, Hunan, Jiangxi, and Fujian are in the stage of survival after transplanting. 
Figure 7: The development of rapeseed in early April 2012 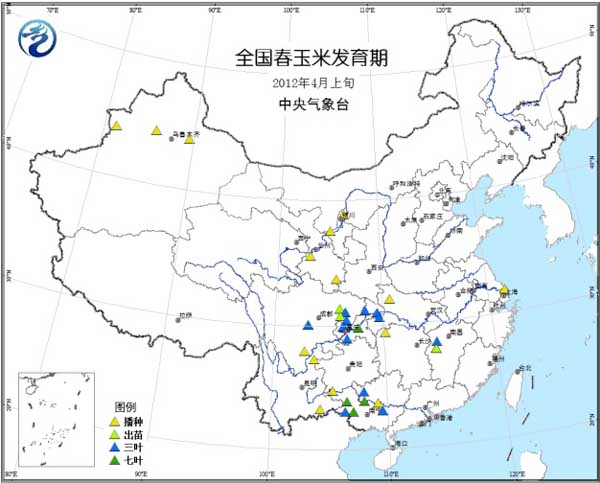
Figure 8 Spring corn development period in early April 2012 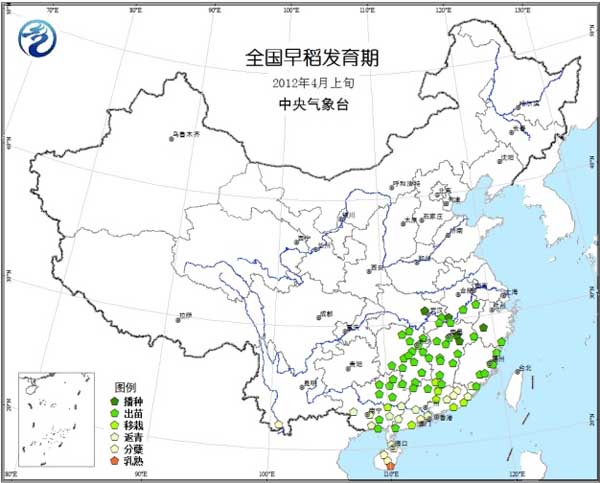
Figure 9 Early rice development in early April 2012 
Figure 10 Rice development period in the first quarter of April, 2012 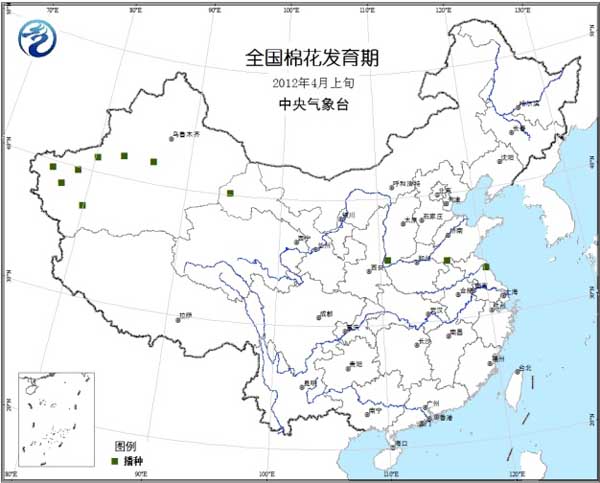
Figure 11 Cotton development period in early April 2012 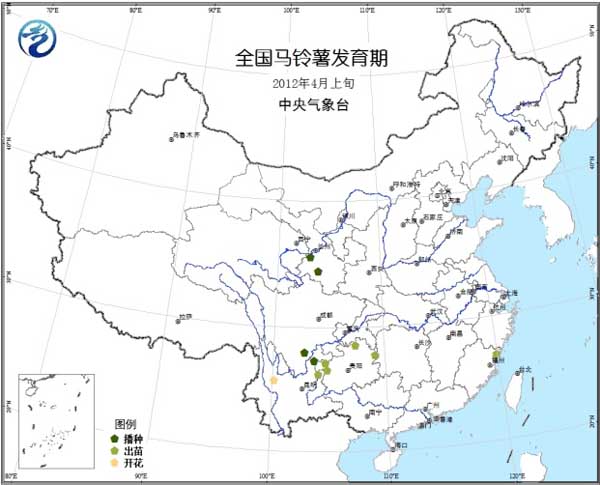
Figure 12 Potato development period in early April 2012
Analysis of Agricultural Meteorological Conditions in Main Agricultural Areas
Northeast China, Inner Mongolia: The temperature in the northeastern part of Inner Mongolia and the eastern part of Inner Mongolia is 2~4°C, which delays the soil thawing, which is not conducive to spring tillage and land preparation. The wind cooling caused by cold air is also not conducive to the spring breeding and facility agriculture production of livestock.
Northwest, North China, Huanghuai: Most of the temperature is 1~4°C, the light is sufficient, the soil moisture is more suitable, which is conducive to winter wheat to green jointing and spring maize, cotton sowing and facility agricultural production. Spring wheat is planted smoothly; but precipitation is less, The windy weather is not conducive to soil conservation, and drought signs appear in parts of western Henan.
Jianghuai and Jianghan: Most of the areas are mainly sunny to cloudy, with suitable soil moisture, which is conducive to winter wheat sowing and booting, rapeseed flowering pods and spring maize, peanut and other spring-sown crops sowing seeds, which is also beneficial to the growth of open field vegetables and facility crops. However, the humidity in the field is high in some areas, which is conducive to the development of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and wheat sheath blight.
Jiangnan and South China: The weather between the weather and the rain is conducive to rice planting, transplanting, replanting and rapeseed, and it is beneficial to the growth and development of spring maize, potato, spring peanut and other crops. By the end of the year, the early rice planting in South China was basically completed; Hunan, Jiangxi, and southern Zhejiang entered the end, and the central part of Zhejiang entered the peak of planting. In the middle of the decade, heavy rains occurred in southern Hunan, eastern Guangxi, and central and western Guangdong. Early rice planting and rapeseed flowering were affected.
Southwest: Sichuan Basin and most of Guizhou Province have high temperature and high light, suitable for soil moisture, which is conducive to summer crop yield formation and spring sowing; 10 to 25 millimeters of precipitation in central and southern Yunnan, 25 to 50 millimeters in some areas, and drought in the central part of the country; There is still no effective precipitation in southern Sichuan, and the drought continues to develop, which is not conducive to the formation of winter wheat and other crops and spring sowing.
Main agricultural meteorological disasters
Drought: The drought in northern Yunnan and southern Sichuan continued to develop, and the yield of winter wheat and other crops in some areas was greatly affected (Figure 13). As of April 10, 41 counties (autonomous regions and municipalities) in 7 cities (autonomous regions) such as Neijiang, Leshan and Zigong in Sichuan Province suffered 285.6 thousand hectares of crops due to drought, of which 26.8 thousand hectares were rejected.
Heavy rains and hail: April 7-9, strong convective weather such as heavy rain, hail and short-term thunderstorms and winds caused flowering and pod formation of rapeseed in southern Hunan, eastern Guangxi, central and western Guangdong, southeastern Yunnan, southern Guizhou and other places. Rice seedling growth, flue-cured tobacco and other local crops and tea gardens and orchards are adversely affected. 
Figure 13 Major agricultural meteorological disasters in early April 2012
Prospects and recommendations for agricultural meteorological conditions in this decade
It is estimated that in the next 10 days, the average daily temperature in the northern winter wheat area will be above 12 °C. At present, the soil moisture is mostly suitable, and the meteorological conditions are generally conducive to the winter wheat jointing and booting; however, the precipitation is less than 5 mm, the temperature is high and the rain is less, and the wheat is needed. As the amount of water increases, soil loss increases. The temperature in the northeast region has risen steadily, and most of them are 1°C higher, which is conducive to soil thawing and preparation for land preparation. Most of the southern part of the rainy weather, there are heavy rains in some areas, most of Hunan, most of Jiangxi, southern Zhejiang, most of Guangdong and eastern Guangxi, soil wetness will continue, for rice seedling growth, rape growth and spring sowing crops The growth is more unfavorable; there is no effective precipitation in northern Yunnan and southern Sichuan, and the drought will continue. Suggest:
The northern spring sowing area should seize the favorable weather and plant at the right time. According to the thawing situation of the soil in the northeast region, the land preparation should be prepared in time and the sowing date should be arranged reasonably. The areas of southwestern Heilongjiang, western Jilin, central and eastern Inner Mongolia, etc., should closely monitor the rain and sentiment, and broadcast in time. Winter wheat in the north will generally enter the jointing and booting stage, which is also a critical period for water demand and fertilizer. All localities should timely water the joint water according to the situation and rational fertilization to promote the formation of yield.
After the rain in the southern region, it is necessary to clear the ditch in time to prevent the danger of strong convective weather. Ensure the smooth start of spring sowing and the normal growth of crops; the rape field should strengthen the management of flowering field to promote the growth of pods and the formation of yield; the rice area should strengthen the management of water and fertilizer in Putian and strive to cultivate strong growth. In southern Sichuan and northern Yunnan, it is still necessary to stand on drought, and seize the favorable opportunity to artificially increase rainfall to ensure timely planting of rice, tobacco seedlings and dry land crops.
In addition, all localities must strengthen the monitoring and prevention of pests and diseases.
Rubber pipe refers to the pipe used for gas transmission, often used in gas welding, gas cutting, various gas welding, plasma arc welding and cutting. There are two kinds of welding rubber pipe, according to the national standard blue pipe for oxygen pipe, the maximum pressure is 1.5mpa; Red tube or black tube for acetylene tube, allow the use of pressure 0.5 ~ I.OMPa. The characteristics of rubber tube are physiological inertia, UV resistance, ozone resistance, high and low temperature resistance (-80 to 300 degrees), high transparency, strong resilience, compression resistance permanent deformation, oil resistance, stamping resistance, acid and alkali resistance, wear resistance, flame resistance, voltage resistance, electrical conductivity and other properties.
Supporting electrical appliances, electronics, furniture equipment, toys, hardware, medical equipment, sporting goods, audio, lighting, machinery, cars, motorcycles, ships, aviation, harsh working environment wire coat comb water, for many materials, can play a role in isolation and other fields of industry.
Hebei Yuanbai Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.yuanbaikeji.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)