The direction of the projection line in the horizontal plane of the line of intersection of the vertical plane intersecting the strike line at right angles to the strike line.
Formation dip angle
The maximum angle between the rock formation and the horizontal plane.
Monoclinic monoclinal strata
A group of rock formations leans in a single direction with a generally uniform tendency, called a monoclinic layer.
Stratigraphic fold
A wavy deformation of tectonic movements in tectonic movements. It has various forms and occurrences, such as anticlines and synclines.
Anticline structure
The rock formations on both sides of the folds tend to face each other, protruding upwards into a bridge shape, with an old nuclear strata and new two-wing strata, called anticline structures.
Diagonal structure syncline
Rock formations on both sides of the fold tend to face each other, concave down into a boat shape, a new nuclear layer, old two-wing strata, said oblique structure.
Fault fault
In the fracture change, relative displacement occurs along the rock masses on both sides of the fracture surface, which is called a fault.
Fault surface
The rift rock is the rupture surface of two discontinuous fault blocks. The relative displacement of the fault block occurs along this surface.
Fault line fault line
The intersection between the fault plane and the ground.
Normal fault
The rock on the upper side of the faulted fault plane is called the upper plate, and the rock on the lower side is called the lower plate. The fault on the lower plate is called the normal fault.
Reverse fault
The rock on the top of the inclined fault plane is called the upper plate, and the rock on the lower side is called the lower plate. The fault on the upper plate is called the reverse fault.
Thrust fault
When the reverse fault fault plane inclination angle is greater than 45°, it is called a thrust fault.
Thrust fault
The reverse fault fault plane tilt angle between 10 ° and 30 ° is called an overthrust.
Break Fault fault throw
After a fault occurs, displacement occurs at the adjacent two points along the cutting plane. The distance between these two points is called the distance.
Fall fault
The vertical distance between two adjacent points after a normal fault occurs.
Landmark horst
In a series of fault combinations, the combination of the two fault blocks descending and the central fault block rising is called a ground barrier.
Grab graben
In a series of fault combinations, the combination of fault blocks on both sides rises and the central fault block descends is called ground mantle.
Traction normal draw
Normal fault An orthorhombic struc- ture formed in the vicinity of the fracture surface, an anticline nose structure formed in the ascending disc, and a descending disc forming a monoclinic inclination or inclination consistent with the section.
Reverse Traction inverse draw
In the normal fault near fault plane, the anticline formed by the descending disc or the oblique direction of the stratum is opposite to the inclined direction of the section.
Fault structure
The faults distributed on a single slope divide the monoclinic into a number of fault blocks that are distributed in a stepped manner and are referred to as a stepped structure.
Nose structure
Anticline folds one end down and the other end lifts up.
Wedge prism is an optical element having plane-inclined surfaces, usually the faces are inclined toward one another at very small angles. Wedges divert light toward their thicker portions.
Wedge prism is commonly used in laser system for eliminating the reflections from the second surface or for beam steering.circle wedge,square wedge,irregular wedge...Every materials,sizes,wedges and coatings may be available by custom orders. Standard and broadband antireflection coatings are available upon request.
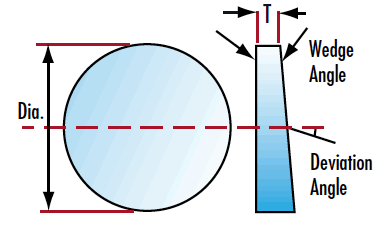
optical wedges
Specification of our wedge prism as follow:
*Material: HK9L Grade A optical glass,Fused Silica JGS1,JGS2,JGS3, or other optical glass materials.
*Dimension Tolerance:+/-0.20mm to +0.01/-0.01mm
*Thickness Tolerance:+/-0.20mm to +/-0.005mm
*Surface Quality:80-50 to 10-5 Scratch/Dig
*Surface Flatness: at 632.8nm lambda to lambda /20 per 25mm
*Clear Aperture:80% -- 100%
*Angle Tolerance:3-5 minutes to 3 second
*Chamfer:0.3+/-0.20mm *45degree
*No Chamfer
*Coating Optional
Wedge Prism,Fused Silica Wedge Prism,Jgs1 Wedge Prisms,N-Bk7 Wedge Prism
China Star Optics Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.opticsrealpoo.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)